The Secondary Structure of a Protein Results From _____.
Whereas the tertiary structure of proteins is defined as the arrangement of secondary structure content in 3-dimensional space. Alpha helices are the most common form of secondary structure in proteins.

Major Differences Com Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes Protein Biology
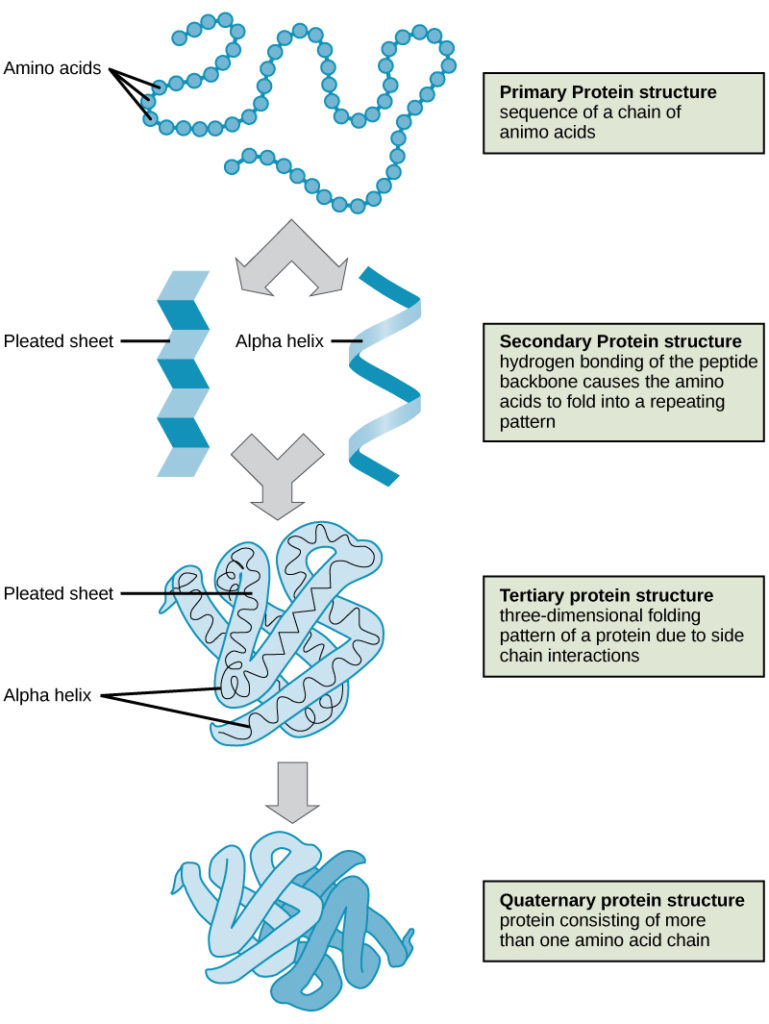
The backbones regular repeating folding patterns are referred to as a proteins secondary structure.
. Hydrogen nonpolar covalent polar covalent ionic hydrogen ---- Secondary structure of proteins ie. The secondary structure of a protein results from _____. Which of the following statements regarding protein structure is false.
The coiling is caused by hydrogen bond. Repetitive hydrogen bonding between amino acid residues to form a 3-dimensional structure. Such structural features result from properties common to all peptide chains.
The secondary structure of proteins results because of _____ bonding between molecules in the protein molecules backbone. Up to 256 cash back Is the primary structure of a 50 kD protein the same or different than the primary structure of the 250 kD protein. PROTEUS2 - is a web server designed to support comprehensive protein structure prediction and structure-based annotation.
The tertiary structure of a protein is the _____ The tertiary structure of a protein is the _____ Which is true of the secondary structure of dna. The backbone just refers to the polypeptide chain apart from the R groups so all we mean here is that secondary structure does not involve R group atoms. Ea formation of disulfide linkages b.
The second major secondary structure element in proteins is the β-sheet. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure. The secondary structure of a protein refers to the way in which protein molecules are coiled and folded in a certain direction on the basis of the primary structure Bolotina et al 1980 and the secondary structure forms a local spatial conformation under.
The secondary structure of proteins is determined by the pattern of hydrogen bonding. The next level of protein structure secondary structure refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone. They are created by right-handed coiling of the primary protein structure.
The structure of Collagen is in Triple helical in structure. The hydrogen bonds form between the partially negative oxygen atom and the partially positive nitrogen atom. Tertiary structure The tertiary structure is the product of the interaction between the side chains R of the amino acids composing the protein.
A large number of server and tools are used to predict the secondary structure analysis. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is called its primary structure. How to identify a rightleft handed helix.
The Secondary Structure Of A Protein Results From - Secondary structure refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone. The primary structure is defined as the sequence of amino acids that compose a polypeptide chain. Alpha-helixes and β-pleated sheets are examples of _____ structure of a protein.
If not explain why not Since the secondary structure of a protein results from hydrogen bonding between components shared by all amino acids a hydrogen on an amide N on one amino acid interacts with an oxygen on the carbony of another amino acid the secondary Structure does not depend on the specific amino acid groups the R-groups in the amino acid chain. The order in which amino acids exist in a protein is known as its primary sequence. Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of local segments of proteinsThe two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets though beta turns and omega loops occur as well.
Formation of hydrogen bonds C formation of salt bridges d more than one response is correct Qe no correct response 6. Proteins structures are made by condensation of amino acids forming peptide bonds. Bonds between sulfur atoms hydrophobic - 54246 karawalsh7123 karawalsh7123 09222017 Chemistry High School answered.
The secondary structure of a protein is due to the folding of the polypeptide chain into different folds due to hydrogen bonding and Vander Waal forces. Coil in direction of right hand fingers with thumb pointed into the helix. The secondary structure of a protein results from _____.
Hydrogen bonds belong to the class of intermolecular forces that arise as a result of a moleculeís dipolar characteristic. From this one can study the secondary structure content of homologous proteins a protein family and highlight its structural patterns. An example of a β-sheet with the stabilizing hydrogen bonds between adjacent strands shown as dotted lines is.
The product of their effects is the secondary structure of the protein. Is the secondary structure of the 50 kD protein the same or different than the secondary structure of the 250 kD protein. It is the principal structural element of the human body and makes up 25 o 33 of all the body protein.
The secondary structure is determined by the dihedral angles of the peptide bonds the tertiary structure by the folding of proteins chains in space. The Secondary structure of collagen is the Rod-shaped molecule and most abundant protein of mammals. Alpha helices beta-pleated sheets is formed to due hydrogen bonds between amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
The region of an enzyme where the substrate molecule fits is called the ea active site b substrate. The secondary structure arises from the hydrogen bonds formed between atoms of the polypeptide backbone. What are the three types of secondary structure.
Proteins are divided into 20 distinct amino acids. PROTEUS2 accepts either single sequences for directed studies or multiple sequences for whole proteome. Explain briefly relating to the structure levels of proteins.
DSSPcont Carter Andersen Rost 2003 and STRIDE Heinig Frishman 2004 are online tools used for understanding the secondary structure. 5 The secondary structure of proteins results primarily from which of the following interactions. β-sheets consist of several β-strands stretched segments of the polypeptide chain kept together by a network of hydrogen bonds between adjacent strands.

Reading Protein Structure Biology Early Release

Biol101 Masteringbiology Ch 3 Flashcards Quizlet
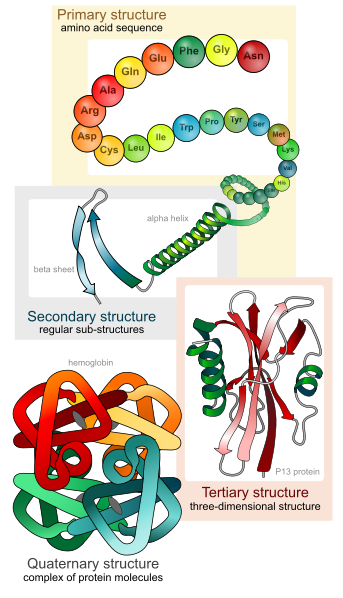
What Are The Primary Secondary Tertiary Structures Of Proteins Socratic
No comments for "The Secondary Structure of a Protein Results From _____."
Post a Comment